In Might, we’ll go deep on cash and financing for a unique style month, by speaking to leaders about where the home loan market is heading and how innovation and organization methods are developing to match the requirements of purchasers now. A prominent brand-new set of awards, called Finest of Financing, debuts this month too, commemorating the leaders in this area. And register for Home Loan Short for weekly updates all year long.
With indications of an economic downturn looming, the Federal Reserve Wednesday authorized what some anticipate will be the last rates of interest boost in the Fed’s year-long inflation-fighting project.
Having actually raised the federal funds rate 10 times given that March 17, 2022, the Federal Free Market Committee has actually now brought its target for the benchmark rate to in between 5.0 to 5.25 percent– a level last seen right before the Great Economic crisis of 2007-09.
Although bond market financiers are wagering the Fed will reverse course and start reducing rates later on this year if an economic downturn does emerge, Federal Reserve Chairman Jerome Powell would just acknowledge that the Fed might be done treking rates in the meantime.
While there are numerous unpredictabilities that lie ahead– consisting of the effects of current bank failures, and a possible deadlock over raising the U.S. financial obligation ceiling– future boosts will depend upon information, Powell stated.
” The evaluation of the level to which extra policy firming might be suitable is going to be a continuous one, conference by conference,” Powell informed press reporters.
In a declaration, members of the policy-setting Federal Free market Committee stated they will watch on “labor market conditions, inflation pressures and inflation expectations, and monetary and worldwide advancements.”
Powell stated the current failures of Silicon Valley Bank, Signature Bank and Very First Republic Bank ” does make complex” tries to determine the cumulative effects of tightening up up until now, which can spend some time to impact financial activity and inflation.
” We have a broad understanding of financial policy,” Powell stated. “Credit tightening up is a various thing. There is a great deal of literature on that. However equating it into rate walkings doubts. Let’s state it includes more unpredictability. We will have the ability to see what’s occurring with credit conditions and occurring with financing. There is a great deal of information on that.”
Of the possibility that Congress will not raise the financial obligation ceiling in time for the U.S. to prevent defaulting on its responsibilities, Powell alerted that the ramifications would be alarming.
” I would simply state I do not actually believe we must even be discussing a world in which the U.S. does not pay its expenses,” the Fed chair stated. “It should not be a thing. And once again I would simply state– nobody needs to presume that the Fed can safeguard the economy and monetary system and our credibility from the damage that such an occasion may cause.”
Ian Shepherdson, primary economic expert at Pantheon Macroeconomics, stated in a note to customers that the Fed has actually currently “done sufficient” to eliminate inflation, which future information is most likely to support reversing course and reducing rates.
” We anticipate the 2 rounds of payroll, CPI, PPI and activity information in between now and the June conference to verify that the economy has actually compromised considerably which inflation pressure is declining, so we believe the Fed will leave rates on hold,” Shepherdson stated. “Keep in mind that it is totally possible that the financial obligation ceiling scenario is at crisis point at the time of the June conference, with markets in chaos, contributing to the case for the Fed not to act. We believe the Fed’s next relocation will be a reducing in September or November.”
Futures markets tracked by the CME FedWatch Tool reveal bond market financiers see a 68 percent possibility that Fed policymakers make one more 25-basis point walking in June, prior to reversing course and beginning to bring the federal funds rate pull back this fall.
On a call with financial investment experts Tuesday, Fannie Mae Chief Financial Officer Chryssa Halley stated financial experts at the home loan huge continue to anticipate a “modest” economic crisis in the 2nd half of 2023, which might be worsened by current bank failures.
” Bank failures are typically part of economic downturns,” Halley stated. “The tension in banking might even more tighten up bank credit conditions, moisten customer and organization self-confidence, and result in lowered customer costs, organization financial investment, and hiring activity.”
However with numerous financial experts likewise anticipating home loan rates to pull away later on this year in anticipation that the Federal Reserve will bring short-term rates pull back, Halley believes real estate might be a brilliant area in the months to come.
The quick boost in house sales in reaction to little rate decreases previously in the very first quarter “highlights our expectation that the bottled-up need in the real estate sector will assist moderate any future economic crisis,” Halley stated.
Home mortgage rates do not constantly track the Fed’s relocations in lockstep, however 10-year Treasurys yields can be a helpful sign of where home loan rates are headed next given that financiers have a comparable cravings for them. Yields on the 10-year federal government bonds have actually decreased today on expectations that the Fed would signify an end to its rate-hike project.
While the Fed might be done raising short-term rates, policymakers stated they’ll continue to relax the Fed’s holdings of mortgage-backed securities (MBS) and long-lasting federal government financial obligation.
The Fed has actually been letting $35 billion in MBS and $60 billion in Treasurys roll off its balance sheet monthly as part of a “quantitative tightening up” strategy introduced last summer season to relax the enormous purchases it made to prop up the economy throughout the pandemic.
That quantitative tightening up is most likely to keep home loan rates from falling too quickly. However financial experts at Fannie Mae and the Home Loan Bankers Association (MBA) do anticipate home loan rates will continue to decrease from 2022 peaks this year and next.
Home mortgage rates anticipated to reduce
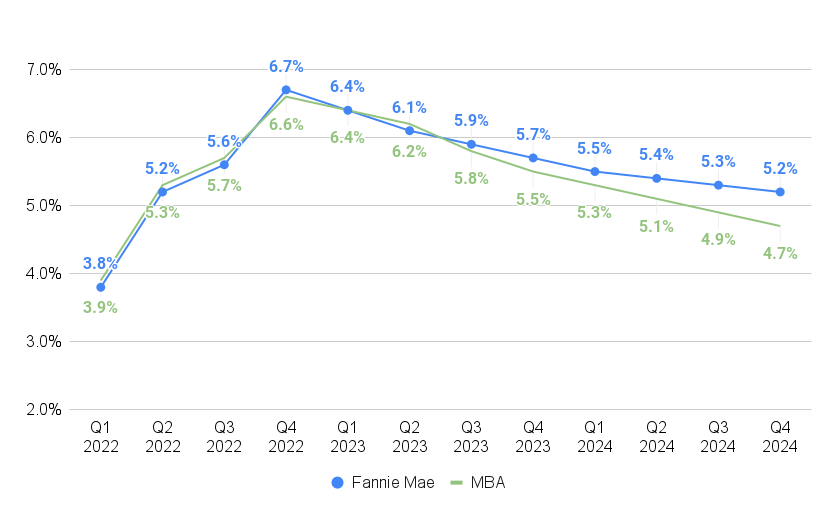
Source: Home Loan Bankers Association, Fannie Mae Real Estate Projection, April 2023
In an April 17 projection, MBA financial experts stated they anticipate rates on 30-year fixed-rate home mortgages to typical 5.5 percent by the 4th quarter of this year and drop listed below 5 percent in the 3rd quarter of next year.
Fannie Mae forecasters do not anticipate rates to dip listed below 5 percent while Federal Reserve policymakers are still examining what the effect of current bank failures and tighter financing conditions will be on inflation.
Get Inman’s Home Loan Short Newsletter provided right to your inbox. A weekly roundup of all the greatest news on the planet of home mortgages and closings provided every Wednesday. Click on this link to subscribe.
